The thrill of launching a brand-new company is undeniable. Many individuals daydream of becoming their own boss, generating their own opportunities, and earning a lot of money, but few really take the plunge. This is because it is often a difficult and frightening endeavor. Building a company from scratch requires a significant investment of time, energy, and money. You'll have to spend a lot of time awake and will likely have to seek outside funding in order to get your firm off the ground. Also, as a designer, store, or restaurant owner, you have a lot more to think about before opening your doors to the general public. If you have the guts to go out on your own and create an eatery, you'll need a business strategy before you do anything else. Find out what elements your company model must have by reading on.
Basics of Business Models
Simply said, a business model is a blueprint for how to launch a successful company. Outlines the company's future offerings to customers, as well as its marketing strategy and financial forecasts. Everything should be profitable in the long run. When developing a company strategy, organizations also factor in the money they'll need to spend.
Companies' business strategies are — and really should be — uniquely crafted for their industry. As an example, a restaurant's model will be distinct from that of a software development firm. There are several essentials that must be included in every business plan for a restaurant. The menu is the most blatant example. The business plan for a restaurant also includes an evaluation of the competition, a marketing tactic, financial forecasts, and an explanation of the restaurant's unique selling offer.
Unique Value Proposition
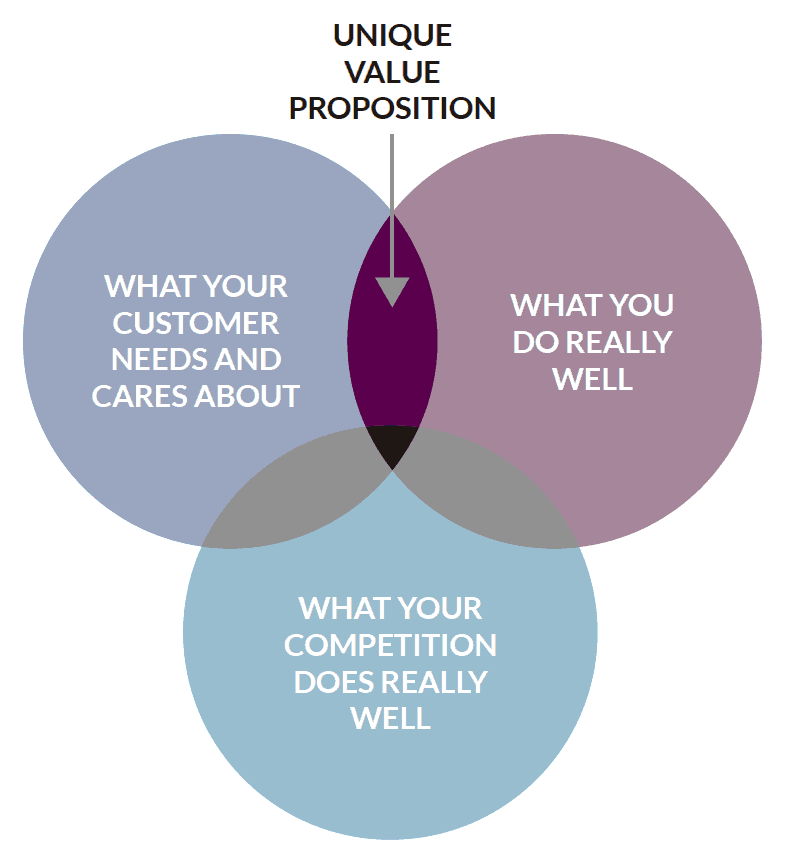
A strong business plan for a restaurant will include a concise explanation of the company's USP. The value proposition describes what the restaurant provides its patrons that cannot be found at other local eateries. Having something that sets you apart from the competition is important for any company, but it's more crucial for a restaurant that has to fight every day to bring in customers. The value proposition of a restaurant may be based on a variety of factors, such as the variety of food offered, the reasonable prices, the quality of service, and the enjoyable ambiance.
The menu is a crucial component of every restaurant's business plan. If a restaurant wants to provide ethnic food that is not served at any other establishment in the neighborhood, the business's value proposition may center on the variety of dishes offered on the menu. Whatever the case may be, a restaurant's menu is a key factor in determining its success. One of the most important factors in a restaurant's ability to predict its expenses, sales, and profits is the decisions it makes while creating its menu.
Target Market
The business model relies heavily on the target market to determine who the company's clients will be. If a business doesn't know its target demographic, it will fail. Of course, eating out is an option as well. To better understand who they could sell to, many businesses invest substantial time and resources. It's not enough to just claim that the company will serve all clients; instead, it must identify the specific age range, economic level, and lifestyle preferences of its ideal clientele. The failure to do so may waste time and, more crucially, money for the eatery.
It is crucial to gauge consumer interest in a product or service before releasing it on a wide scale or before launching the product. This is why many fast food restaurants like McDonald's &'' Burger King experiment with new menu items in a small market before introducing them nationwide. If the product does well, it should be distributed to additional markets. If not, the company may slow down the rollout with little to no monetary loss.
Marketing &'' Competition
Before operating their own restaurant, both seasoned and aspiring owners need to take the time to research the options available to them. Aspiring restaurant operators might get valuable insight from those already operating in the industry. It might be helpful to get insight into the methods used by the competitors.
- Analyze the market's strengths and shortcomings.
- Products and services are made more appealing by the new owner.
- Resulting in competitive pricing.
- Formulation of an effective advertising plan.
The restaurant's approach to reaching its target demographic and, as a result, achieving its financial objectives is referred to as its marketing strategy. Promotional activities are any kind of paid or unpaid activity aimed at acquiring or keeping clients. Offering catering and other value-added services are examples of the kinds of things that may fall within a restaurant's marketing umbrella. There are a variety of resources that may assist with table management and the upkeep of a busy restaurant. It is possible for guests to book a table online and for the restaurant staff to be notified of any changes (cancellations or no-shows) thanks to restaurant reservation technology. A waitlist and other tools to aid in the organization of catered events are two examples of the types of services offered.
Costs and Forecasts
Any viable company plan will have forecasts of both initial capital requirements and ongoing income and expenditures. The importance of this factor in the success of a restaurant is emphasized once again. While certain restaurants debut to great fanfare and immediately draw a steady clientele, many take a while to do so. The costs of running a restaurant are substantial. Costs are for everything from food and drink to paper goods, cutlery, furniture, utilities, salaries, and marketing. The initial investment for a restaurant might vary greatly across different concepts. The business plan for a restaurant has to be specific about the total amount and origin of outside funding. Furthermore, the restaurant's plan for maintaining profitability should include a detailed breakdown of its anticipated continuing expenditures, sales, and profit margin.
watch next


